Portal:World
The World Portal

The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind.
Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God, or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world, while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole, or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole, and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles - show another
- Image 1Human security is a paradigm for understanding global vulnerabilities whose proponents challenge the traditional notion of national security through military security by arguing that the proper referent for security should be at the human rather than the national level. Human security reveals a people-centred and multi-disciplinary understanding of security which involves a number of research fields, including development studies, international relations, strategic studies, and human rights. The United Nations Development Programme's 1994 Human Development Report is considered a milestone publication in the field of human security, with its argument that ensuring "freedom from want" and "freedom from fear" for all persons is the best path to tackle the problem of global insecurity.
Critics of the concept argue that its vagueness undermines its effectiveness, that it has become little more than a vehicle for activists wishing to promote certain causes, and that it does not help the research community understand what security means or help decision-makers to formulate good policies. Alternatively, other scholars have argued that the concept of human security should be broadened to encompass military security: 'In other words, if this thing called 'human security' has the concept of 'the human' embedded at the heart of it, then let us address the question of the human condition directly. Thus understood, human security would no longer be the vague amorphous add-on to harder-edged areas of security such as military security or state security.' (Full article...) - Image 2Pacific Ocean of Earth seen from space in 1969
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as oceans (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic Ocean), and are themselves mostly divided into seas, gulfs and subsequent bodies of water. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water and is the primary component of Earth's hydrosphere, acting as a huge reservoir of heat for Earth's energy budget, as well as for its carbon cycle and water cycle, forming the basis for climate and weather patterns worldwide. The ocean is essential to life on Earth, harbouring most of Earth's animals and protist life, originating photosynthesis and therefore Earth's atmospheric oxygen, still supplying half of it.
Ocean scientists split the ocean into vertical and horizontal zones based on physical and biological conditions. Horizontally the ocean covers the oceanic crust, which it shapes. Where the ocean meets dry land it covers relatively shallow continental shelfs, which are part of Earth's continental crust. Human activity is mostly coastal with high negative impacts on marine life. Vertically the pelagic zone is the open ocean's water column from the surface to the ocean floor. The water column is further divided into zones based on depth and the amount of light present. The photic zone starts at the surface and is defined to be "the depth at which light intensity is only 1% of the surface value" (approximately 200 m in the open ocean). This is the zone where photosynthesis can occur. In this process plants and microscopic algae (free-floating phytoplankton) use light, water, carbon dioxide, and nutrients to produce organic matter. As a result, the photic zone is the most biodiverse and the source of the food supply which sustains most of the ocean ecosystem. Light can only penetrate a few hundred more meters; the rest of the deeper ocean is cold and dark (these zones are called mesopelagic and aphotic zones). (Full article...) - Image 3

Gerardus Mercator 1512–1594
The Mercator world map of 1569 is titled Nova et Aucta Orbis Terrae Descriptio ad Usum Navigantium Emendate Accommodata (Renaissance Latin for "New and more complete representation of the terrestrial globe properly adapted for use in navigation"). The title shows that Gerardus Mercator aimed to present contemporary knowledge of the geography of the world and at the same time 'correct' the chart to be more useful to sailors. This 'correction', whereby constant bearing sailing courses on the sphere (rhumb lines) are mapped to straight lines on the plane map, characterizes the Mercator projection. While the map's geography has been superseded by modern knowledge, its projection proved to be one of the most significant advances in the history of cartography, inspiring the 19th century map historian Adolf Nordenskiöld to write "The master of Rupelmonde stands unsurpassed in the history of cartography since the time of Ptolemy." The projection heralded a new era in the evolution of navigation maps and charts and it is still their basis.The map is inscribed with a great deal of text. The framed map legends (or cartouches) cover a wide variety of topics: a dedication to his patron and a copyright statement; discussions of rhumb lines; great circles and distances; comments on some of the major rivers; accounts of fictitious geography of the north pole and the southern continent. The full Latin texts and English translations of all the legends are given below. Other minor texts are sprinkled about the map. They cover such topics as the magnetic poles, the prime meridian, navigational features, minor geographical details, the voyages of discovery and myths of giants and cannibals. These minor texts are also given below. (Full article...) - Image 4The Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS) is an industry taxonomy developed in 1999 by MSCI and Standard & Poor's (S&P) for use by the global financial community. The GICS structure consists of 11 sectors, 25 industry groups, 74 industries and 163 sub-industries into which S&P has categorized all major public companies. The system is similar to ICB (Industry Classification Benchmark), a classification structure maintained by FTSE Group.
GICS is used as a basis for S&P and MSCI indexes used in the financial field which each company is assigned to a sub-industry, and to an industry, industry group, and sector, by its principal business activity. "GICS" is a registered trademark of McGraw Hill Financial and MSCI Inc. (Full article...) - Image 5
Around the World in Eighty Days (French: Le Tour du monde en quatre-vingts jours) is an adventure novel by the French writer Jules Verne, first published in French in 1872. In the story, Phileas Fogg of London and his newly employed French valet Passepartout attempt to circumnavigate the world in 80 days on a wager of £20,000 (equivalent to £2.3 million in 2023) set by his friends at the Reform Club. It is one of Verne's most acclaimed works. (Full article...) - Image 6

Juno in the Underworld by Jan Brueghel the Younger, between 1626 and 1630
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld.
The concept of an underworld is found in almost every civilization and "may be as old as humanity itself". Common features of underworld myths are accounts of living people making journeys to the underworld, often for some heroic purpose. Other myths reinforce traditions that the entrance of souls to the underworld requires a proper observation of ceremony, such as the ancient Greek story of the recently dead Patroclus haunting Achilles until his body could be properly buried for this purpose. People with high social status were dressed and equipped in order to better navigate the underworld. (Full article...) - Image 7The BWF World Tour is a Grade 2 badminton tournament series, sanctioned by Badminton World Federation (BWF). It is a competition open to the top world ranked players in singles (men's and women's) and doubles (men's, women's and mixed). The competition was announced on 19 March 2017 and came into effect starting from 2018, replacing the BWF Super Series, which was held from 2007 to 2017.
The BWF World Tour are divided into six levels, namely World Tour Finals, Super 1000, Super 750, Super 500, and Super 300 in order (part of the HSBC World Tour). One other category of tournament, the BWF Tour Super 100 level, also offers ranking points. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
- Image 1Japanese depiction of a Portuguese carrack, a result of globalizing maritime trade
- Image 213th-century French historiated initial with the three classes of medieval society: those who prayed (the clergy), those who fought (the knights), and those who worked (the peasantry)
- Image 4An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as far as it is today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
- Image 5An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
- Image 6A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
- Image 7A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
- Image 8Earth's history with time-spans of the eons to scale. Ma means "million years ago". (from History of Earth)
- Image 9Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
- Image 10Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
- Image 12A pillar at Neolithic Göbekli Tepe
- Image 14Cuneiform inscription, eastern Turkey
- Image 17Shanghai. China urbanized rapidly in the 21st century.
- Image 18Portrait of Alfraganus in the Compilatio astronomica, 1493. Islamic astronomers began just before the 9th century to collect and translate Indian, Persian and Greek astronomical texts, adding their own astronomy and enabling later, particularly European astronomy to build on. Symbolic for the post-classical period, a period of an increasing trans-regional literary culture, particularly in the sciences, spreading and building on methods of science. (from Human history)
- Image 19Empires of the world in 1898
- Image 20Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
- Image 22Earth's land use for human agriculture in 2019 (from Earth)
- Image 24A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
- Image 25Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
- Image 26A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
- Image 28Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
- Image 32A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
- Image 33Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
- Image 34Earth's night-side upper atmosphere appearing from the bottom as bands of afterglow illuminating the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to the orange and faintly green line of the lowest airglow, at about one hundred kilometers at the edge of space and the lower edge of the thermosphere (invisible). Continuing with green and red bands of aurorae stretching over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
- Image 35Fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989
- Image 40The first airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
- Image 41Successive dispersals of Homo erectus (yellow), Homo neanderthalensis (ochre) during Out of Africa I and Homo sapiens (red, Out of Africa II), with the numbers of years since they appeared before present. (from Human history)
- Image 42A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
- Image 44An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
- Image 46Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
- Image 47The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
- Image 48Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
- Image 50Benin Bronze head from Nigeria
- Image 51Obelisk of Axum, Ethiopia
- Image 52Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
- Image 54A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
- Image 55A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
- Image 57Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
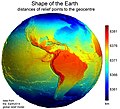
- Image 58Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
- Image 59One of the eleven Rock-hewn Churches of Lalibela constructed during the Zagwe dynasty in Ethiopia (from Human history)
- Image 60Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
- Image 61Angkor Wat temple complex, Cambodia, early 12th century
- Image 63Olmec colossal head, now at the Museo de Antropología de Xalapa
- Image 64Atomic bombing of Nagasaki, 1945
- Image 66Battle during the 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
- Image 67Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
- Image 68A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
- Image 69Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
- Image 71Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
- Image 72The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
- Image 73Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
- Image 74Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
- Image 76A reconstruction of Pannotia (550 Ma). (from History of Earth)
- Image 77Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
- Image 80Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
- Image 81Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
- Image 82Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
- Image 83Notre-Dame de Paris, France
- Image 85Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
- Image 86A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
- Image 87Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
Megacities of the world - show another
Guangzhou, previously romanized as Canton or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about 120 km (75 mi) northwest of Hong Kong and 145 km (90 mi) north of Macau, Guangzhou has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the Silk Road.
The port of Guangzhou serves as a transportation hub for Guangzhou, one of China's three largest cities. Guangzhou was captured by the British during the First Opium War and no longer enjoyed a monopoly after the war; consequently it lost trade to other ports such as Hong Kong and Shanghai, but continued to serve as a major entrepôt. Following the Second Battle of Chuenpi in 1841, the Treaty of Nanking was signed between Sir Robert Peel on behalf of Queen Victoria and Lin Zexu on behalf of Emperor Xuanzong and ceded Hong Kong to the United Kingdom on 26 January 1841 after the agreement of the Convention of Chuenpi. (Full article...)
Did you know - load new batch

- ... that from 1912, Jindřiška Flajšhansová was the principal editor of Ženské listy, a Czech journal that became a women's "survival manual" during World War I?
- ... that the heads of the world's largest producer of pure lithium grew up in poverty?
- ... that the 2026 FIFA World Cup final will be hosted by a stadium that is cutting corners?
- ... that Fred J. Wiseman delivered the world's first unofficial airmail flight by airplane?
- ... that the adoption of the Declaration of Independence of Azerbaijan made the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic the first successful republic in the Muslim world?
- ... that the hashtag #AlDubEBTamangPanahon set a Guinness World Record in 2015 with 40,706,392 uses in 24 hours, coinciding with the television event "Tamang Panahon"?
- ... that in 2017 the British travel magazine Wanderlust rated Azerbaijan's electronic visa as the easiest visa to obtain in the world?
- ... that Alda Milner-Barry, the older sister of World War II Enigma codebreaker Stuart Milner-Barry, worked for British military intelligence during World War I?
Countries of the world - show another

Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean to its south and southwest. It has a population of around 5.5 million and covers an area of 43,000 square miles (111,369 km2). The official language is English. Over 20 indigenous languages are spoken, reflecting the country's ethnic and cultural diversity. The capital and largest city is Monrovia.
Liberia began in the early 19th century as a project of the American Colonization Society (ACS), which believed that black people would face better chances for freedom and prosperity in Africa than in the United States. Between 1822 and the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861, more than 15,000 freed and free-born African Americans, along with 3,198 Afro-Caribbeans, relocated to Liberia. Gradually developing an Americo-Liberian identity, the settlers carried their culture and tradition with them while colonizing the indigenous population. Led by the Americo-Liberians, Liberia declared independence on July 26, 1847, which the U.S. did not recognize until February 5, 1862. (Full article...)

The Seven Wonders of Ukraine (Ukrainian: Сім чудес України, romanized: Sim chudes Ukraïny [ˈsʲim tʃʊˈdɛs ʊkrɐˈjinɪ]) are seven historical and cultural monuments of Ukraine, which were chosen in the Seven Wonders of Ukraine contest held in July, 2007. This was the first public contest of that kind which was followed by the Seven Natural Wonders of Ukraine, the Seven Wonderful Routes of Ukraine, and the Seven Wonderful Castles of Ukraine. All nominated sites are publicly owned protected areas of at least regional level, available for tourism.
The voting for all contests consisted of two parts: experts in Ukraine voted for their seven best sites, and internet users voted for their seven favorite sites on the official website. (Full article...)
Related portals
Protected areas of the world - load new batch
- Image 1

The Valley of the Giants skywalk at Walpole-Nornalup National Park
Western Australia is the second largest country subdivision in the world.
As of 2022, based on the latest Collaborative Australian Protected Areas Database report, it contains 1857 separate land-based protected areas with a total area of 76,142,710 hectares (188,152,700 acres), accounting for just over 30 percent of the state's land mass. By area, Indigenous Protected Areas account for the largest part of this, almost 67 percent while, by number, nature reserves hold the majority with two-third of all land-based protected areas being nature reserves. (Full article...) - Image 2This is a list of protected areas of Ontario that are administered by Government of Ontario. Ontario Parks and the Ministry of the Environment, Conservation and Parks are the provincial bodies responsible for managing these protected areas. (Full article...)
- Image 3Protected areas of Slovenia include one national park (Slovene: narodni park), three regional parks (regijski park), several natural parks (krajinski park), and hundreds of natural monuments (naravni spomenik) and monuments of designed nature (spomenik oblikovane narave). They cover about 12.5% of the Slovenian territory. Under the Wild Birds Directive, 26 sites totalling roughly 25% of the nation's land are "Special Protected Areas"; the Natura 2000 proposal would increase the totals to 260 sites and 32% of national territory. (Full article...)
- Image 4

Network of protected areas in Albania (2020)
Despite being a relatively small country, Albania is exceedingly rich in biodiversity. Its ecosystems and habitats support over 5,550 species of vascular and non-vascular plants and more than 15,600 species of coniferous and non-coniferous evergreens, most of which are threatened at global and European levels. The country has made recent efforts to expand its network of protected areas which now include: 11 national parks, 1 marine park, 718 nature monuments, 23 managed nature reserves, 11 protected landscapes, 4 World Heritage Sites, 4 Ramsar sites and other protected areas of various categories, that when combined, account for 21.36% of the territory. Furthermore, a biosphere reserve, 45 important plant areas and 16 important bird areas are found in the country.
Meanwhile, the central government has proclaimed the Coastline and the Tirana Greenbelt as areas of national importance. (Full article...) - Image 5

The northernmost tip of Prins Karls Forland in Forlandet National Park
Svalbard is an Arctic wilderness archipelago comprising the northernmost part of Norway. There are twenty-nine protected natural areas, consisting of seven national parks, six nature reserves, fifteen bird sanctuaries and one geotope protected area. In addition, human traces dating from before 1946 are automatically protected. The protected areas make up 39,800 square kilometers (15,400 sq mi) or 65% of the land area, and 78,000 square kilometers (30,000 sq mi) or 86.5% of the territorial waters. The largest protected areas are Nordaust-Svalbard Nature Reserve and Søraust-Svalbard Nature Reserve, which cover most of the areas east of the main island of Spitsbergen, including the islands of Nordaustlandet, Edgeøya, Barentsøya, Kong Karls Land and Kvitøya. Six of the national parks are located on Spitsbergen. Ten of the bird sanctuaries and the Moffen Nature Reserve are located within national parks. Five of the bird sanctuaries are Ramsar sites and fourteen of the bird sanctuaries are islands. Svalbard is on Norway's tentative list for nomination as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The supreme responsibility for conservation lies with the Norwegian Ministry of the Environment, which has delegated the management to the Governor of Svalbard and the Norwegian Directorate for Nature Management. The foundation for conservation was established in the Svalbard Treaty of 1920, and has been further specified in the Svalbard Environmental Act of 2001. The first round of protection took force on 1 July 1973, when most of the current protected areas came into effect. This included the two large nature reserves and three of the national parks. Moffen Nature Reserve was established in 1983, followed by four national parks, three nature reserves and one geotope protection area between 2002 and 2005. (Full article...) - Image 6The Ulyanovsk Oblast in Russia contains about 118 protected natural areas. (Full article...)
- Image 7

Rock carvings at the Ewaninga Rock Carvings Conservation Reserve
The protected areas of the Northern Territory consists of protected areas managed by the governments of the Northern Territory and Australia and private organisations with a reported total area of 335,527 square kilometres (129,548 sq mi) being 24.8% of the total area of the Northern Territory of Australia. (Full article...) - Image 8
- Image 9

Centre for Nature Education at the Białowieża National Park, Poland
Protected areas of Poland include the following categories, as defined by the Act on Protection of Nature (Polish: Ustawa o ochronie przyrody) of 16 April 2004, by the Polish Parliament: (Full article...) - Image 10

Map of protected areas of the Czech Republic: national parks (grey) and protected landscape areas (green)
There are several types of protected areas of the Czech Republic. The main form of landscape protection is delimitation of special protected areas. All the types of protected areas are determined by law. (Full article...) - Image 11

Upolu Island, Samoa
This is a list of some protected areas of Samoa which include national parks, reservations, protected nature zones, marine reserves and other areas of significant biodiversity and conservation.
In 1994, Samoa ratified the international and legally binding treaty, the Convention on Biological Diversity to develop national strategies for conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity. In 2010, protected areas in the country cover 5% of land although the government aims to increase protected areas coverage to 15%. (Full article...) - Image 12This is a list of protected areas in Botswana. (Full article...)
- Image 13

Map of Georgia
The protected areas of Georgia cover almost one million acres (4,000 km2) of the state. These areas are managed by different federal and state level authorities and receive varying levels of protection. Some areas are managed as wilderness while others are operated with acceptable commercial exploitation. On the Federal level, Georgia contains 1 Biosphere Reserve, 15 National Park Service Managed Sites, 1 National Forest and 8 Wildlife Refuges. Georgia is home to 63 state parks, 48 of which are state parks and 15 that are National Historic Sites, and many state wildlife preserves, under the supervision of the Georgia Department of Parks and Recreation, a division of the Georgia Department of Natural Resources. (Full article...) - Image 14Protected areas of Canada consist of approximately 12.1 percent of the nation's landmass and freshwater are considered conservation areas, including 11.4 percent designated as protected areas. Approximately 13.8 percent of Canada's territorial waters are conserved, including 8.9 percent designated as protected areas. Terrestrial areas conserved have increased by 65 percent in the 21st century, while marine areas conserved have increased by more than 3,800 percent.
Conservation and protected areas have different mandates depending on the organization which manages them, with some areas having a greater focus on ecological integrity, historical preservation, public usage, scientific research, or a combination of usages. Some areas such as the Polar Bear Pass, are co-managed and overseen by government and local indigenous agencies. (Full article...) - Image 15
Selected world maps
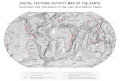
- Image 1Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
- Image 2Time zones of the world
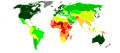
- Image 3United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
- Image 4Mollweide projection of the world
- Image 5Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
- Image 6The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
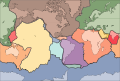
- Image 7A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
- Image 8The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
- Image 91516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
Continents of Earth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Cenozoic Era (present–66.0 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic Era (66.0–252 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Paleozoic Era (252–539 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Proterozoic Eon (539 Ma–2.5 Ga) |
| ||||||||||||
| Archean Eon (2.5–4 Ga) | |||||||||||||
| Hadean Eon (4–4.6 Ga) | |||||||||||||
ka = kiloannum (thousand years ago); Ma = megaannum (million years ago); Ga = gigaannum (billion years ago). See also: Geologic time scale • | |||||||||||||
| City proper | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan area | |
| Urban area/agglomeration | |
| Historical | |
| Related articles | |
| Locations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Related | ||
| Retrospectively recognized expositions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIE-recognized Universal expositions | |||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized specialized expositions |
| ||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized horticultural exhibitions (AIPH) | |||||||||||||
| Not BIE- recognized |
| ||||||||||||
†Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||||||||
| Confederations | |
|---|---|
| World Championships | |
| World Cup | |
| Special events | |
| Presidents |
|
| Awards | |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Economic classification of countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-World Model | |||||
| Gross domestic product (GDP) |
| ||||
| Gross national income (GNI) | |||||
| Wages | |||||
| Wealth | |||||
| Other national accounts | |||||
| Human development | |||||
| Digital divide | |||||
| Net international investment position (NIIP) | |||||
| Technological |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociological | |||||
| Ecological |
| ||||
| Biological |
| ||||
| Astronomical | |||||
| Eschatological |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Fictional | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| Theatres |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Principal participants |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspects |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus